Thanks to the reduction of launch costs, the number of satellites in orbit is overgrowing.
New companies arise and develop new ways of using space assets.
This is primarily due to the design of cheaper rocket launchers and satellite mass production. Therefore, the budget required for a launch is decreasing, allowing the space industries to invest more in the satellite.
That’s why many companies deploy different mega-constellations. Moreover, the space asset’s opening to private companies leads to the implementation of less expensive projects than the previous national space projects.
Looking at this scenario, a tool dedicated to the design and optimization of satellite constellations becomes essential.

Existing applications are complex and general purpose-driven; therefore, adapting them to strict requirements for designing a specific constellation is time-consuming.
Instead, ORBIT WIZARD aims to solve this problem by offering an easy-to-use solution.
ORBIT WIZARD supports the developing phase of a constellation project. Thanks to its advanced algorithms, ORBIT WIZARD searches for optimal parameters that fit the user’s operational constraints, such as the minimum number of satellites required to provide worldwide Coverage to a location or a user-defined area.
ORBIT WIZARD has different modules for various constellation design-related problems; it can be used to search for optimal orbital parameters on a single plane or optimize an existing constellation; moreover, it can aid in designing formation flying missions.
Constellations are typically composed of several structurally identical satellites. If for any valid reason, during the development of the satellite, a structural change must be introduced, the overall constellation performance will be affected.
In this kind of scenario, our tool provides fast feedback to evaluate the impact of the changes introduced.
FEATURES:
ORBIT WIZARD is divided into two parts:
ORBIT DESIGNER module (OD)
It defines and analyzes performances of one or more “classic” reference orbits;
CONSTELLATION DESIGNER module (COD)
Optimizes the constellation design starting from relevant mission requirements (e.g., satellite number minimization without affecting the overall performance).
ORBIT DESIGN MODULE calculation purpose is to find optimal orbits for:
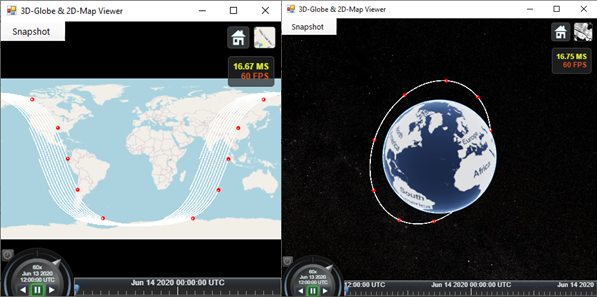
CONSTELLATION DESIGN MODULE allows users to choose among the most common space mission requirements, and it is divided into two sections:
1 – COD FOR REMOTE SENSING: constellation designer aimed to optimize constellations constrained by ground track repetitiveness or revisit time performances.
This tool allows users to choose among three constellation design types:
2 – COD FOR COVERAGE: constellation designer aimed to optimize constellations committed to global or regional coverage.
The tool provides the user with functions useful to optimize specific types of constellations, such as:
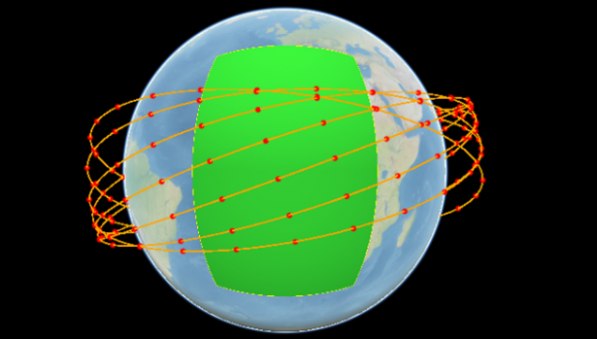
The user can define the following mission approaches:
COD FOR COVERAGE Tool also provides an optimization function, COVERAGE AND OPTIMAL INCLINATION ANALYSIS, which, by taking the input values computed by other available functions we can try to maximize the continuous, worldwide or regional, n-degree Coverage, and find the most efficient solution from a range of possible inclination values defined by the user.
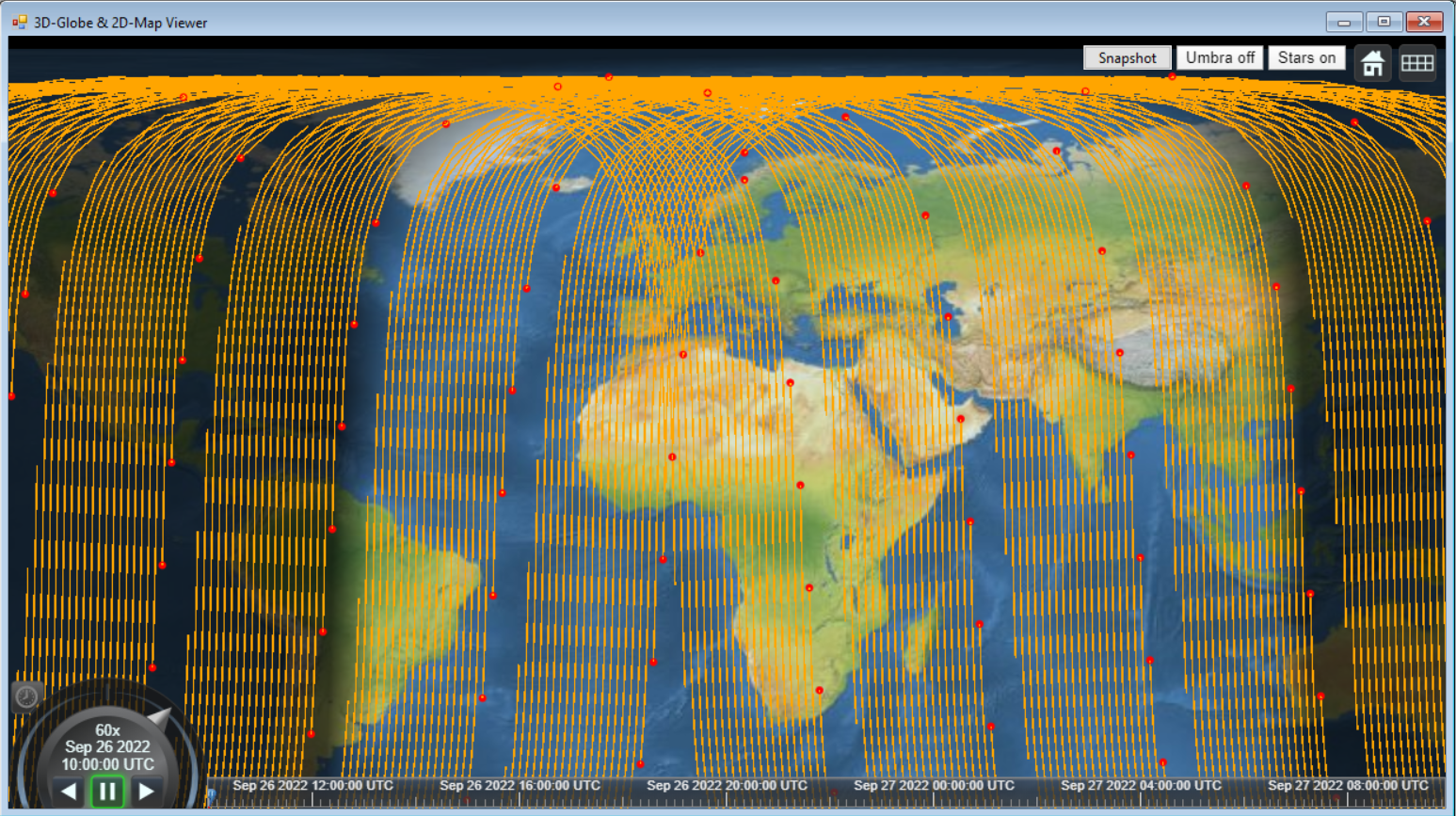
The capability to design and analyze a satellite constellation makes ORBIT WIZARD an effective planning tool for any constellation development.
ORBIT WIZARD is suitable for enterprises involved in designing and deploying constellations, such as communication companies.
If the goal is to improve coverage performance, the tool allows for optimizing the final amount of satellites and, consequently, the project’s overall cost.
© 2022 GMSpazio s.r.l. All rights reserved. Partita I.V.A.: 08473031006 | Cookie policy